Lesson type
Difficulty level
This is the first of two workshops on reproducibility in science, during which participants are introduced to concepts of FAIR and open science. After discussing the definition of and need for FAIR science, participants are walked through tutorials on installing and using Github and Docker, the powerful, open-source tools for versioning and publishing code and software, respectively.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:20:58
Speaker: : Erin Dickie and Sejal Patel
Course:
In this lesson, while learning about the need for increased large-scale collaborative science that is transparent in nature, users also are given a tutorial on using Synapse for facilitating reusable and reproducible research.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:15:12
Speaker: : Abhi Pratap
This lesson contains the first part of the lecture Data Science and Reproducibility. You will learn about the development of data science and what the term currently encompasses, as well as how neuroscience and data science intersect.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 32:18
Speaker: : Ariel Rokem
In this second part of the lecture Data Science and Reproducibility, you will learn how to apply the awareness of the intersection between neuroscience and data science (discussed in part one) to an understanding of the current reproducibility crisis in biomedical science and neuroscience.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 31:31
Speaker: : Ashley Juavinett
Course:
The lecture provides an overview of the core skills and practical solutions required to practice reproducible research.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:25:17
Speaker: : Fernando Perez
Course:
This lecture provides an introduction to reproducibility issues within the fields of neuroimaging and fMRI, as well as an overview of tools and resources being developed to alleviate the problem.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:03:07
Speaker: : Russell Poldrack
Course:
This lecture provides a historical perspective on reproducibility in science, as well as the current limitations of neuroimaging studies to date. This lecture also lays out a case for the use of meta-analyses, outlining available resources to conduct such analyses.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 55:39
Speaker: : Angela Laird
This workshop will introduce reproducible workflows and a range of tools along the themes of organisation, documentation, analysis, and dissemination.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 01:28:43
Speaker: :
This lecture covers the ethical implications of the use of brain-computer interfaces, brain-machine interfaces, and deep brain stimulation to enhance brain functions and was part of the Neuro Day Workshop held by the NeuroSchool of Aix Marseille University.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:02:00
Speaker: : Jens Clausen
Course:
This module covers many types of invasive neurotechnology devices/interfaces for the central and peripheral nervous systems. Invasive neurotech devices are crucial, as they often provide the greatest accuracy and long-term use applicability.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 9:40
Speaker: : Colin Fausnaught
Course:
This lesson is a general overview of overarching concepts in neuroinformatics research, with a particular focus on clinical approaches to defining, measuring, studying, diagnosing, and treating various brain disorders. Also described are the complex, multi-level nature of brain disorders and the data associated with them, from genes and individual cells up to cortical microcircuits and whole-brain network dynamics. Given the heterogeneity of brain disorders and their underlying mechanisms, this lesson lays out a case for multiscale neuroscience data integration.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:09:33
Speaker: : Sean Hill
This lesson gives an in-depth introduction of ethics in the field of artificial intelligence, particularly in the context of its impact on humans and public interest. As the healthcare sector becomes increasingly affected by the implementation of ever stronger AI algorithms, this lecture covers key interests which must be protected going forward, including privacy, consent, human autonomy, inclusiveness, and equity.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:22:06
Speaker: : Daniel Buchman
This is a continuation of the talk on the cellular mechanisms of neuronal communication, this time at the level of brain microcircuits and associated global signals like those measureable by electroencephalography (EEG). This lecture also discusses EEG biomarkers in mental health disorders, and how those cortical signatures may be simulated digitally.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:11:04
Speaker: : Etay Hay
This is the second of three lectures around current challenges and opportunities facing neuroinformatic infrastructure for handling sensitive data.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 48:26
Speaker: : Michael Schirner
In this lesson you will learn about current efforts towards integrating multimodal human brain data using the open source SCORE HED library schema.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 23:29
Speaker: : Dora Hermes
This lecture aims to help researchers, students, and health care professionals understand the place for neuroinformatics in the patient journey using the exemplar of an epilepsy patient.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:32:53
Speaker: : Randy Gollub & Prantik Kundu
The lesson introduces the Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS), the community standard for organizing, curating, and sharing neuroimaging and associated data. The session focuses on understanding the BIDS framework, learning its data structure and validation processes.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 38:52
Speaker: : Cyril Pernet
This session moves from BIDS basics into analysis workflows, focusing on how to turn raw, BIDS-organized data into derivatives using BIDS Apps and containers for reproducible processing. It compares end-to-end pipelines across fMRI and PET (and notes EEG/MEG), explains typical preprocessing choices, and shows how standardized inputs plus containerized tools (Docker/AppTainer) yield consistent, auditable outputs.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 56:03
Speaker: : Martin Nørgaard
The session explains GDPR rules around data sharing for research in Europe, the distinction between law and ethics, and introduces practical solutions for securely sharing sensitive datasets. Researchers have more flexibility than commonly assumed: scientific research is considered a public interest task, so explicit consent for data sharing isn’t legally required, though transparency and informing participants remain ethically important. The talk also introduces publicneuro.eu, a controlled-access platform that enables sharing neuroimaging datasets with open metadata, DOIs, and customizable access restrictions while ensuring GDPR compliance.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 31:12
Speaker: : Cyril Pernet
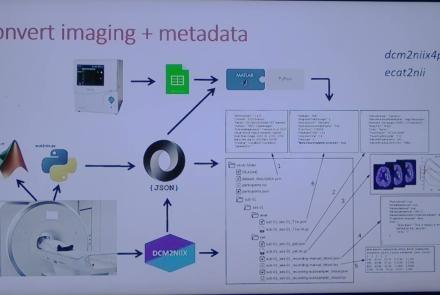
This session introduces the PET-to-BIDS (PET2BIDS) library, a toolkit designed to simplify the conversion and preparation of PET imaging datasets into BIDS-compliant formats. It supports multiple data types and formats (e.g., DICOM, ECAT7+, nifti, JSON), integrates seamlessly with Excel-based metadata, and provides automated routines for metadata updates, blood data conversion, and JSON synchronization. PET2BIDS improves human readability by mapping complex reconstruction names into standardized, descriptive labels and offers extensive documentation, examples, and video tutorials to make adoption easier for researchers.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 9:23
Speaker: : Cyril Pernet
Topics
- Artificial Intelligence (7)
- Philosophy of Science (5)
- Provenance (3)
- protein-protein interactions (1)
- Extracellular signaling (1)
- Animal models (8)
- Assembly 2021 (29)
- Brain-hardware interfaces (14)
- Clinical neuroscience (40)
- International Brain Initiative (2)
- Repositories and science gateways (11)
- Resources (6)
- General neuroscience
(62)
- Neuroscience (11)
- Cognitive Science (7)
- Cell signaling (6)
- Brain networks (11)
- Glia (1)
- Electrophysiology (41)
- Learning and memory (5)
- Neuroanatomy (24)
- Neurobiology (16)
- Neurodegeneration (1)
- Neuroimmunology (1)
- Neural networks (15)
- Neurophysiology (27)
- Neuropharmacology (2)
- Neuronal plasticity (16)
- Synaptic plasticity (4)
- Visual system (12)
- Phenome (1)
- General neuroinformatics
(27)
- Computational neuroscience (279)
- Statistics (7)
- Computer Science (21)
- Genomics (34)
- Data science
(34)
- Open science (61)
- Project management (8)
- Education (4)
- Publishing (4)
- Neuroethics (42)