Lesson type
Difficulty level
This video gives a brief introduction to Neuro4ML's lessons on neuromorphic computing - the use of specialized hardware which either directly mimics brain function or is inspired by some aspect of the way the brain computes.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 3:56
Speaker: : Dan Goodman
In this lesson, you will learn in more detail about neuromorphic computing, that is, non-standard computational architectures that mimic some aspect of the way the brain works.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 10:08
Speaker: : Dan Goodman
This video provides a very quick introduction to some of the neuromorphic sensing devices, and how they offer unique, low-power applications.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 2:37
Speaker: : Dan Goodman
Course:
This lecture covers modeling the neuron in silicon, modeling vision and audition, and sensory fusion using a deep network.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:32:17
Speaker: : Shih-Chii Liu
This lesson presents a simulation software for spatial model neurons and their networks designed primarily for GPUs.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 21:15
Speaker: : Tadashi Yamazaki
This lesson gives an overview of past and present neurocomputing approaches and hybrid analog/digital circuits that directly emulate the properties of neurons and synapses.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 41:57
Speaker: : Giacomo Indiveri
Presentation of the Brian neural simulator, where models are defined directly by their mathematical equations and code is automatically generated for each specific target.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 20:39
Speaker: : Giacomo Indiveri
The lecture covers a brief introduction to neuromorphic engineering, some of the neuromorphic networks that the speaker has developed, and their potential applications, particularly in machine learning.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 19:57
Speaker: : Runchun Mark Wang
This lecture provides an introduction to optogenetics, a biological technique to control the activity of neurons or other cell types with light.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 39:34
Speaker: : Adam Packer
Course:
This primer on optogenetics primer discusses how to manipulate neuronal populations with light at millisecond resolution and offers possible applications such as curing the blind and "playing the piano" with cortical neurons.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 59:06
Speaker: : Clay Reid
The lesson introduces the Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS), the community standard for organizing, curating, and sharing neuroimaging and associated data. The session focuses on understanding the BIDS framework, learning its data structure and validation processes.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 38:52
Speaker: : Cyril Pernet
This session moves from BIDS basics into analysis workflows, focusing on how to turn raw, BIDS-organized data into derivatives using BIDS Apps and containers for reproducible processing. It compares end-to-end pipelines across fMRI and PET (and notes EEG/MEG), explains typical preprocessing choices, and shows how standardized inputs plus containerized tools (Docker/AppTainer) yield consistent, auditable outputs.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 56:03
Speaker: : Martin Nørgaard
The session explains GDPR rules around data sharing for research in Europe, the distinction between law and ethics, and introduces practical solutions for securely sharing sensitive datasets. Researchers have more flexibility than commonly assumed: scientific research is considered a public interest task, so explicit consent for data sharing isn’t legally required, though transparency and informing participants remain ethically important. The talk also introduces publicneuro.eu, a controlled-access platform that enables sharing neuroimaging datasets with open metadata, DOIs, and customizable access restrictions while ensuring GDPR compliance.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 31:12
Speaker: : Cyril Pernet
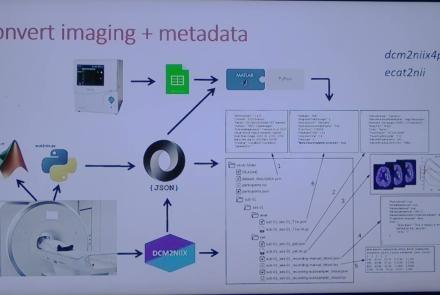
This session introduces the PET-to-BIDS (PET2BIDS) library, a toolkit designed to simplify the conversion and preparation of PET imaging datasets into BIDS-compliant formats. It supports multiple data types and formats (e.g., DICOM, ECAT7+, nifti, JSON), integrates seamlessly with Excel-based metadata, and provides automated routines for metadata updates, blood data conversion, and JSON synchronization. PET2BIDS improves human readability by mapping complex reconstruction names into standardized, descriptive labels and offers extensive documentation, examples, and video tutorials to make adoption easier for researchers.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 9:23
Speaker: : Cyril Pernet
This session introduces the PET-to-BIDS (PET2BIDS) library, a toolkit designed to simplify the conversion and preparation of PET imaging datasets into BIDS-compliant formats. It supports multiple data types and formats (e.g., DICOM, ECAT7+, nifti, JSON), integrates seamlessly with Excel-based metadata, and provides automated routines for metadata updates, blood data conversion, and JSON synchronization. PET2BIDS improves human readability by mapping complex reconstruction names into standardized, descriptive labels and offers extensive documentation, examples, and video tutorials to make adoption easier for researchers.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 41:04
Speaker: : Martin Nørgaard
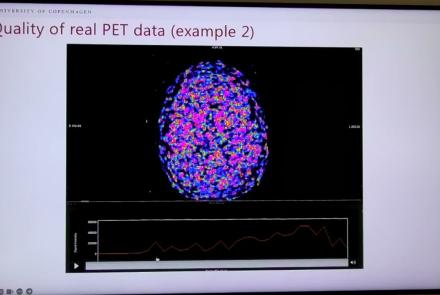
This session dives into practical PET tooling on BIDS data—showing how to run motion correction, register PET↔MRI, extract time–activity curves, and generate standardized PET-BIDS derivatives with clear QC reports. It introduces modular BIDS Apps (head-motion correction, TAC extraction), a full pipeline (PETPrep), and a PET/MRI defacer, with guidance on parameters, outputs, provenance, and why Dockerized containers are the reliable way to run them at scale.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:05:38
Speaker: : Martin Nørgaard
This session introduces two PET quantification tools—bloodstream for processing arterial blood data and kinfitr for kinetic modeling and quantification—built to work with BIDS/BIDS-derivatives and containers. Bloodstream fuses autosampler and manual measurements (whole blood, plasma, parent fraction) using interpolation or fitted models (incl. hierarchical GAMs) to produce a clean arterial input function (AIF) and whole-blood curves with rich QC reports ready. TAC data (e.g., from PETPrep) and blood (e.g., from bloodstream) can be ingested using kinfitr to run reproducible, GUI-driven analyses: define combined ROIs, calculate weighting factors, estimate blood–tissue delay, choose and chain models (e.g., 2TCM → 1TCM with parameter inheritance), and export parameters/diagnostics. Both are available as Docker apps; workflows emphasize configuration files, reports, and standard outputs to support transparency and reuse.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:20:56
Speaker: : Granville Matheson
Learn how to create a standard extracellular electrophysiology dataset in NWB using Python.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 23:10
Speaker: : Ryan Ly
Learn how to create a standard calcium imaging dataset in NWB using Python.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 31:04
Speaker: : Ryan Ly
In this tutorial, you will learn how to create a standard intracellular electrophysiology dataset in NWB using Python.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 20:23
Speaker: : Pamela Baker
Topics
- Artificial Intelligence (7)
- Philosophy of Science (5)
- Provenance (3)
- protein-protein interactions (1)
- Extracellular signaling (1)
- Animal models (8)
- Assembly 2021 (29)
- Brain-hardware interfaces (14)
- Clinical neuroscience (40)
- International Brain Initiative (2)
- Repositories and science gateways (11)
- Resources (6)
- General neuroscience
(62)
- Neuroscience (11)
- Cognitive Science (7)
- Cell signaling (6)
- Brain networks (11)
- Glia (1)
- Electrophysiology (41)
- Learning and memory (5)
- Neuroanatomy (24)
- Neurobiology (16)
- Neurodegeneration (1)
- Neuroimmunology (1)
- Neural networks (15)
- Neurophysiology (27)
- Neuropharmacology (2)
- Neuronal plasticity (16)
- Synaptic plasticity (4)
- Visual system (12)
- Phenome (1)
- General neuroinformatics
(27)
- Computational neuroscience (279)
- Statistics (7)
- Computer Science (21)
- Genomics (34)
- Data science
(34)
- Open science (61)
- Project management (8)
- Education (4)
- Publishing (4)
- Neuroethics (42)