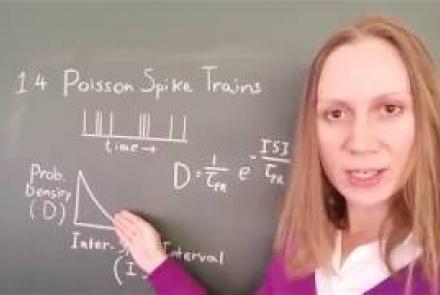Lesson type
Difficulty level
This lesson describes spike timing-dependent plasticity (STDP), a biological process that adjusts the strength of connections between neurons in the brain, and how one can implement or mimic this process in a computational model. You will also find links for practical exercises at the bottom of this page.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 12:50
Speaker: : Dan Goodman
This lesson provides a brief introduction to the Computational Modeling of Neuronal Plasticity.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 0:40
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
In this lesson, you will be introducted to a type of neuronal model known as the leaky integrate-and-fire (LIF) model.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:23
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson goes over various potential inputs to neuronal synapses, loci of neural communication.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:20
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson describes the how and why behind implementing integration time steps as part of a neuronal model.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:08
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
In this lesson, you will learn about neural spike trains which can be characterized as having a Poisson distribution.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:18
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson covers spike-rate adaptation, the process by which a neuron's firing pattern decays to a low, steady-state frequency during the sustained encoding of a stimulus.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:26
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson provides a brief explanation of how to implement a neuron's refractory period in a computational model.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 0:42
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
In this lesson, you will learn a computational description of the process which tunes neuronal connectivity strength, spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP).
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 2:40
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson reviews theoretical and mathematical descriptions of correlated spike trains.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 2:54
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson investigates the effect of correlated spike trains on spike-timing dependent plasticity (STDP).
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:43
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson goes over synaptic normalisation, the homeostatic process by which groups of weighted inputs scale up or down their biases.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 2:58
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
In this lesson, you will learn about the intrinsic plasticity of single neurons.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 2:08
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson covers short-term facilitation, a process whereby a neuron's synaptic transmission is enhanced for a short (sub-second) period.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:58
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson describes short-term depression, a reduction of synaptic information transfer between neurons.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:40
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson briefly wraps up the course on Computational Modeling of Neuronal Plasticity.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 0:37
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson describes the current state of brain-computer interface (BCI) standards, including the present obstacles hindering the forward movement of BCI standardization as well as future steps aimed at solving this problem.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 15:01
Speaker: : Martijn de Neeling
This lecture covers the ethical implications of the use of brain-computer interfaces, brain-machine interfaces, and deep brain stimulation to enhance brain functions and was part of the Neuro Day Workshop held by the NeuroSchool of Aix Marseille University.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:02:00
Speaker: : Jens Clausen
Course:
Panel discussion by leading scientists, engineers and philosophers discuss what brain-computer interfaces are and the unique scientific and ethical challenges they pose. hosted by Lynne Malcolm from ABC Radio National's All in the Mind program and features:
- Dr Hannah Maslen, Deputy Director, Oxford Uehiro Centre for Practical Ethics, University of Oxford
- Prof. Eric Racine, Director, Pragmatic Health Ethics Research Unity, Montreal Institute of Clinical Research
- Prof Jeffrey Rosenfeld, Director, Monash Institute of Medical Engineering, Monash University
- Dr Isabell Kiral-Kornek, AI and Life Sciences Researcher, IBM Research
- A/Prof Adrian Carter, Neuroethics Program Coordinator, ARC Centre of Excellence for Integrative Brain Function
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:14:34
Course:
In this module you will learn the basics of Brain Computer Interface (BCI). You will read an introduction to the different technologies available, the main components and steps required for BCI, associated safety and ethical issues, as well as an overview about the future of the field.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 11:02
Speaker: : Colin Fausnaught
Topics
- Artificial Intelligence (7)
- Philosophy of Science (5)
- Provenance (3)
- protein-protein interactions (1)
- Extracellular signaling (1)
- Animal models (8)
- Assembly 2021 (29)
- Brain-hardware interfaces (14)
- Clinical neuroscience (40)
- International Brain Initiative (2)
- Repositories and science gateways (11)
- Resources (6)
- General neuroscience
(62)
- Neuroscience (11)
- Cognitive Science (7)
- Cell signaling (6)
- Brain networks (11)
- Glia (1)
- Electrophysiology (41)
- Learning and memory (5)
- Neuroanatomy (24)
- Neurobiology (16)
- Neurodegeneration (1)
- Neuroimmunology (1)
- Neural networks (15)
- Neurophysiology (27)
- Neuropharmacology (2)
- (-) Neuronal plasticity (16)
- Synaptic plasticity (4)
- Visual system (12)
- Phenome (1)
- General neuroinformatics
(27)
- Computational neuroscience (279)
- Statistics (7)
- Computer Science (21)
- Genomics (34)
- Data science
(34)
- Open science (61)
- Project management (8)
- Education (4)
- Publishing (4)
- Neuroethics (42)