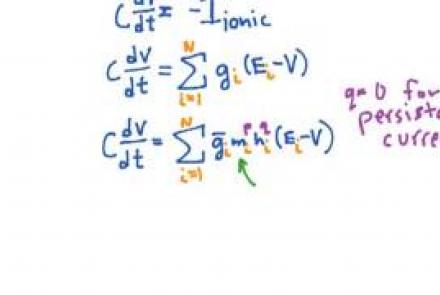Lesson type
Difficulty level
In this lesson you will learn about ion channels and the movement of ions across the cell membrane, one of the key mechanisms underlying neuronal communication.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 25:51
Speaker: : Carl Petersen
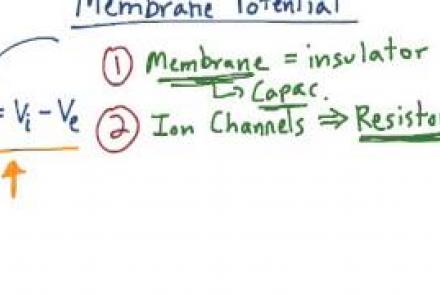
This lesson introduces the membrane potential equation
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 08:16
Speaker: : Alex Williams
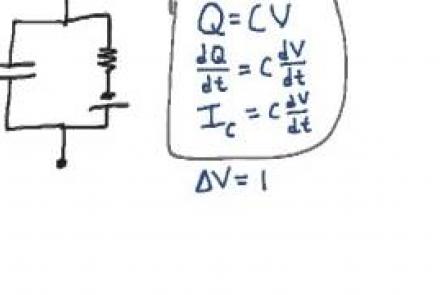
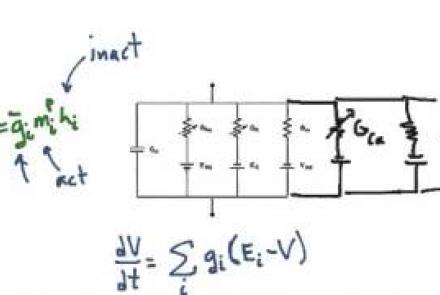
Explanation of the equivalent circuit model for a patch of passive neural membrane.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 9:22
Speaker: : Alex Williams
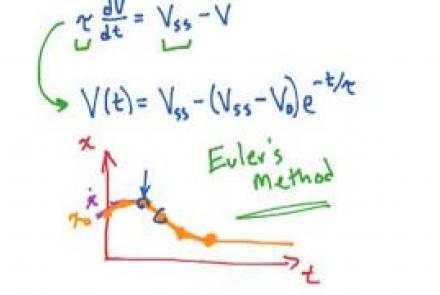
Solving the passive membrane equation
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 4:04
Speaker: : Alex Williams
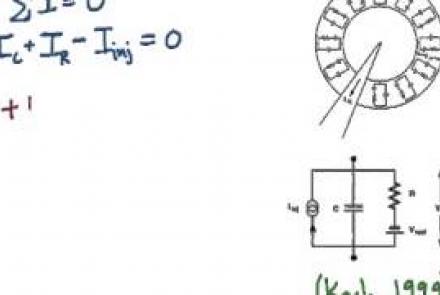
Injecting current into a passive membrane
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 5:54
Speaker: : Alex Williams
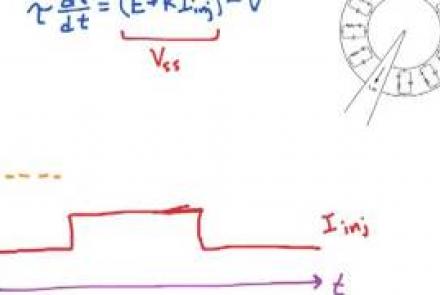
Explains the logic behind dealing with more complex currents by solving the membrane equation numerically.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 9:55
Speaker: : Alex Williams
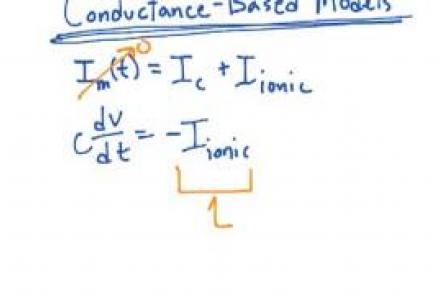
Introducing voltage-dependent ion channels into the passive membrane
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 8:32
Speaker: : Alex Williams
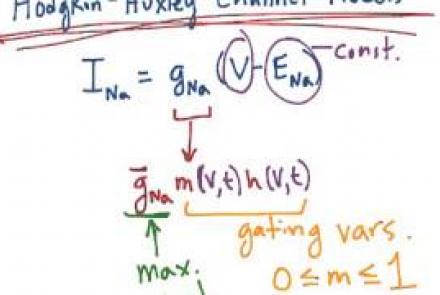
Introducing Hodgkin & Huxley's voltage dependent ion channel models, with emphasis on the sodium conductance
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 10:32
Speaker: : Alex Williams
Introducing the classical Hodgkin & Huxley squid axon model with sodium and potassium conductances
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 9:56
Speaker: : Alex Williams
This lesson extends the conductance-based model equation to multiple neuronal compartments, taking more complex morphology into account.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 9:23
Speaker: : Alex Williams
In this opening lesson, you will hear from the chair of the workshop (Neuroinformatics 2014 in Leiden, Netherlands), who gives an introduction and motivating argument underscoring the importance of collaboration in computational neuroscience.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 8:34
Speaker: : Angus Silver
This lesson gives an introduction to OpenWorm: an open-source project dedicated to creating a virtual C. elegans nematode in a computer.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 23:26
Speaker: : Stephen Larson
The Open Source Brain (OSB) initiative (http://www.opensourcebrain.org) has been created to address the issues of poor accessibility, transparency, validation, and reuse of models in computational neuroscience.This lecture covers the aims of the Open Source Brain initiative, the current functionality of the website, and the range of models already available, and future plans for the project.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 25:32
Speaker: : Padraig Gleeson
This lecture covers NeuronUnit, a library that builds upon SciUnit and integrates with several existing neuroinformatics resources to support validating single-neuron models using data gathered by neurophysiologists.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 17:21
Speaker: : Richard Gerkin
This lesson provides an introduction to the NeuroElectro project, which aims to organize information on cellular neurophysiology.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 17:41
Speaker: : Shreejoy Tripathy
In this lecture, the speaker demonstrates Neurokernel's module interfacing feature by using it to integrate independently developed models of olfactory and vision LPUs based upon experimentally obtained connectivity information.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 29:56
Speaker: : Aurel A. Lazar
The Virtual Brain (TVB) is an open-source, multi-scale, multi-modal brain simulation platform. In this lesson, you get introduced to brain simulation in general and to TVB in particular. This lesson also presents the newest approaches for clinical applications of TVB - that is, for stroke, epilepsy, brain tumors, and Alzheimer’s disease - and show how brain simulation can improve diagnostics, therapy, and understanding of neurological disease.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:35:08
Speaker: : Petra Ritter
This lesson explains the mathematics of neural mass models and their integration to a coupled network. You will also learn about bifurcation analysis, an important technique in the understanding of non-linear systems and as a fundamental method in the design of brain simulations. Lastly, the application of the described mathematics is demonstrated in the exploration of brain stimulation regimes.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:49:24
Speaker: : Andreas Spiegler
In this lesson, the simulation of a virtual epileptic patient is presented as an example of advanced brain simulation as a translational approach to deliver improved clinical results. You will learn about the fundamentals of epilepsy, as well as the concepts underlying epilepsy simulation. By using an iPython notebook, the detailed process of this approach is explained step by step. In the end, you are able to perform simple epilepsy simulations your own.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:28:53
Speaker: : Julie Courtiol
Topics
- Artificial Intelligence (7)
- Philosophy of Science (5)
- Provenance (3)
- protein-protein interactions (1)
- Extracellular signaling (1)
- Animal models (8)
- Assembly 2021 (29)
- Brain-hardware interfaces (14)
- Clinical neuroscience (40)
- International Brain Initiative (2)
- Repositories and science gateways (11)
- Resources (6)
- General neuroscience
(62)
- Neuroscience (11)
- Cognitive Science (7)
- Cell signaling (6)
- Brain networks (11)
- Glia (1)
- Electrophysiology (41)
- Learning and memory (5)
- Neuroanatomy (24)
- Neurobiology (16)
- Neurodegeneration (1)
- Neuroimmunology (1)
- Neural networks (15)
- Neurophysiology (27)
- Neuropharmacology (2)
- Neuronal plasticity (16)
- Synaptic plasticity (4)
- Visual system (12)
- Phenome (1)
- General neuroinformatics
(27)
- (-) Computational neuroscience (279)
- Statistics (7)
- Computer Science (21)
- Genomics (34)
- Data science
(34)
- Open science (61)
- Project management (8)
- Education (4)
- Publishing (4)
- Neuroethics (42)