Lesson type
Difficulty level
Course:
This lesson introduces the EEGLAB toolbox, as well as motivations for its use.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 15:32
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
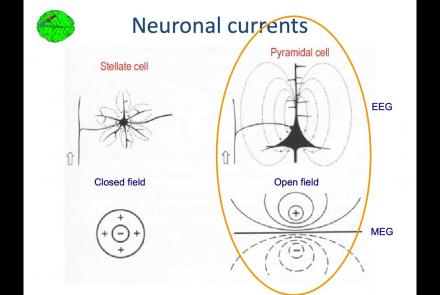
In this lesson, you will learn about the biological activity which generates and is measured by the EEG signal.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 6:53
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
This lesson goes over the characteristics of EEG signals when analyzed in source space (as opposed to sensor space).
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 10:56
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
This lesson describes the development of EEGLAB as well as to what extent it is used by the research community.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 6:06
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
This lesson provides instruction as to how to build a processing pipeline in EEGLAB for a single participant.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 9:20
Speaker: :
Course:
Whereas the previous lesson of this course outlined how to build a processing pipeline for a single participant, this lesson discusses analysis pipelines for multiple participants simultaneously.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 10:55
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
In addition to outlining the motivations behind preprocessing EEG data in general, this lesson covers the first step in preprocessing data with EEGLAB, importing raw data.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 8:30
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
Continuing along the EEGLAB preprocessing pipeline, this tutorial walks users through how to import data events as well as EEG channel locations.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 11:53
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
This tutorial demonstrates how to re-reference and resample raw data in EEGLAB, why such steps are important or useful in the preprocessing pipeline, and how choices made at this step may affect subsequent analyses.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 11:48
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
In this tutorial, users learn about the various filtering options in EEGLAB, how to inspect channel properties for noisy signals, as well as how to filter out specific components of EEG data (e.g., electrical line noise).
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 10:46
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
This tutorial instructs users how to visually inspect partially pre-processed neuroimaging data in EEGLAB, specifically how to use the data browser to investigate specific channels, epochs, or events for removable artifacts, biological (e.g., eye blinks, muscle movements, heartbeat) or otherwise (e.g., corrupt channel, line noise).
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 5:08
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
This tutorial provides instruction on how to use EEGLAB to further preprocess EEG datasets by identifying and discarding bad channels which, if left unaddressed, can corrupt and confound subsequent analysis steps.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 13:01
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
Users following this tutorial will learn how to identify and discard bad EEG data segments using the MATLAB toolbox EEGLAB.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 11:25
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
This module covers many of the types of non-invasive neurotech and neuroimaging devices including electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG), electroneurography (ENG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), and more.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 13:36
Speaker: : Harrison Canning
Hierarchical Event Descriptors (HED) fill a major gap in the neuroinformatics standards toolkit, namely the specification of the nature(s) of events and time-limited conditions recorded as having occurred during time series recordings (EEG, MEG, iEEG, fMRI, etc.). Here, the HED Working Group presents an online INCF workshop on the need for, structure of, tools for, and use of HED annotation to prepare neuroimaging time series data for storing, sharing, and advanced analysis.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 03:37:42
Speaker: :
This lecture covers advanced concept of energy based models. The lecture is a part of the Advanced energy based models modules of the the Deep Learning Course at NYU's Center for Data Science. Prerequisites for this course include: Energy-Based Models I, Energy-Based Models II, Energy-Based Models III, and an Introduction to Data Science or a Graduate Level Machine Learning course.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 56:41
Speaker: : Alfredo Canziani
Course:
This lesson gives an introduction to deep learning, with a perspective via inductive biases and emphasis on correctly matching deep learning to the right research questions.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 01:35:12
Speaker: : Blake Richards
Course:
As a part of NeuroHackademy 2021, Noah Benson gives an introduction to Pytorch, one of the two most common software packages for deep learning applications to the neurosciences.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 00:50:40
Speaker: :
Course:
Learn how to use TensorFlow 2.0 in this full tutorial for beginners. This course is designed for Python programmers looking to enhance their knowledge and skills in machine learning and artificial intelligence.
Throughout the 8 modules in this course you will learn about fundamental concepts and methods in ML & AI like core learning algorithms, deep learning with neural networks, computer vision with convolutional neural networks, natural language processing with recurrent neural networks, and reinforcement learning.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 06:52:07
Speaker: :
Course:
In this hands-on tutorial, Dr. Robert Guangyu Yang works through a number of coding exercises to see how RNNs can be easily used to study cognitive neuroscience questions, with a quick demonstration of how we can train and analyze RNNs on various cognitive neuroscience tasks. Familiarity of Python and basic knowledge of Pytorch are assumed.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 00:26:38
Speaker: :
Topics
- Artificial Intelligence (6)
- Philosophy of Science (5)
- Provenance (2)
- protein-protein interactions (1)
- Extracellular signaling (1)
- Animal models (6)
- Assembly 2021 (29)
- Brain-hardware interfaces (13)
- Clinical neuroscience (17)
- International Brain Initiative (2)
- Repositories and science gateways (11)
- Resources (6)
- General neuroscience
(45)
- Neuroscience (9)
- Cognitive Science (7)
- Cell signaling (3)
- Brain networks (4)
- Glia (1)
- Electrophysiology (16)
- Learning and memory (3)
- Neuroanatomy (17)
- Neurobiology (7)
- Neurodegeneration (1)
- Neuroimmunology (1)
- Neural networks (4)
- Neurophysiology (22)
- Neuropharmacology (2)
- Synaptic plasticity (2)
- Visual system (12)
- Phenome (1)
- General neuroinformatics
(15)
- Computational neuroscience (195)
- Statistics (2)
- Computer Science (15)
- Genomics (26)
- Data science
(24)
- Open science (56)
- Project management (7)
- Education (3)
- Publishing (4)
- Neuroethics (37)