Lesson type
Difficulty level
In this talk, you will learn about the standardization schema for data formats among two of the US BRAIN Initiative networks: the Cell Census Network (BICCN) and the Cell Atlas Network (BICAN).
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 14:58
Speaker: : Michael Hawrylycz
This lesson describes the current state of brain-computer interface (BCI) standards, including the present obstacles hindering the forward movement of BCI standardization as well as future steps aimed at solving this problem.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 15:01
Speaker: : Martijn de Neeling
Course:
Brief introduction to Research Resource Identifiers (RRIDs), persistent and unique identifiers for referencing a research resource.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:30
Speaker: : Anita Bandrowski
Research Resource Identifiers (RRIDs) are ID numbers assigned to help researchers cite key resources (e.g., antibodies, model organisms, and software projects) in biomedical literature to improve the transparency of research methods.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:01:36
Speaker: : Maryann Martone
Course:
The Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS) is a standard prescribing a formal way to name and organize MRI data and metadata in a file system that simplifies communication and collaboration between users and enables easier data validation and software development through using consistent paths and naming for data files.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 0:56
Speaker: : Jean-Babtiste Poline
Course:
Neurodata Without Borders (NWB) is a data standard for neurophysiology that provides neuroscientists with a common standard to share, archive, use, and build common analysis tools for neurophysiology data.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:11
Speaker: : Ben Dichter
Course:
The Neuroimaging Data Model (NIDM) is a collection of specification documents that define extensions the W3C PROV standard for the domain of human brain mapping. NIDM uses provenance information as means to link components from different stages of the scientific research process from dataset descriptors and computational workflow, to derived data and publication.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 0:53
Speaker: : Jean-Babtiste Poline
Course:
This lesson provides a brief introduction to the Neuroscience Information Exchange (NIX) Format data model, which allows storing fully annotated scientific datasets, i.e., data combined with rich metadata and their relations in a consistent, comprehensive format.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:03
Speaker: : Thomas Wachtler
This lecture provides an overview of successful open-access projects aimed at describing complex neuroscientific models, and makes a case for expanded use of resources in support of reproducibility and validation of models against experimental data.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:00:39
Speaker: : Sharon Crook
This lecture provides an introduction to the Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS), a standard for organizing human neuroimaging datasets.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 56:49
Speaker: : Chris Gorgolewski
This lesson provides an overview of Neurodata Without Borders (NWB), an ecosystem for neurophysiology data standardization. The lecture also introduces some NWB-enabled tools.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 29:53
Speaker: : Oliver Ruebel
Course:
This lesson outlines Neurodata Without Borders (NWB), a data standard for neurophysiology which provides neuroscientists with a common standard to share, archive, use, and build analysis tools for neurophysiology data.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 29:53
Speaker: : Oliver Ruebel
In February 2020, the Canadian government published its "Roadmap for Open Science" to provide overarching principles and recommendations to guide Open Science activities in federally funded scientific research. It outlines broad guidelines for making science in Canada open to all while respecting privacy, security, ethical considerations, and appropriate intellectual property protection.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration:
Speaker: :
Course:
This lecture covers the rationale for developing the DAQCORD, a framework for the design, documentation, and reporting of data curation methods in order to advance the scientific rigour, reproducibility, and analysis of data.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 17:08
Speaker: : Ari Ercole
Course:
This tutorial demonstrates how to use PyNN, a simulator-independent language for building neuronal network models, in conjunction with the neuromorphic hardware system SpiNNaker.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 25:49
Speaker: : Christian Brenninkmeijer
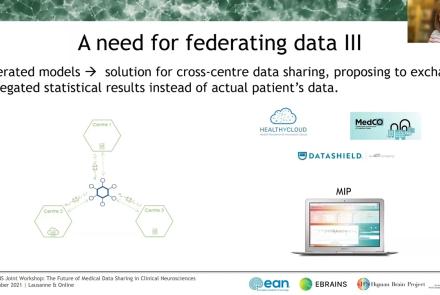
In this session the Medical Informatics Platform (MIP) federated analytics is presented. The current and future analytical tools implemented in the MIP will be detailed along with the constructs, tools, processes, and restrictions that formulate the solution provided. MIP is a platform providing advanced federated analytics for diagnosis and research in clinical neuroscience research. It is targeting clinicians, clinical scientists and clinical data scientists. It is designed to help adopt advanced analytics, explore harmonized medical data of neuroimaging, neurophysiological and medical records as well as research cohort datasets, without transferring original clinical data. It can be perceived as a virtual database that seamlessly presents aggregated data from distributed sources, provides access and analyze imaging and clinical data, securely stored in hospitals, research archives and public databases. It leverages and re-uses decentralized patient data and research cohort datasets, without transferring original data. Integrated statistical analysis tools and machine learning algorithms are exposed over harmonized, federated medical data.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 15:05
Speaker: : Giorgos Papanikos
The Medical Informatics Platform (MIP) is a platform providing federated analytics for diagnosis and research in clinical neuroscience research. The federated analytics is possible thanks to a distributed engine that executes computations and transfers information between the members of the federation (hospital nodes). In this talk the speaker will describe the process of designing and implementing new analytical tools, i.e. statistical and machine learning algorithms. Mr. Sakellariou will further describe the environment in which these federated algorithms run, the challenges and the available tools, the principles that guide its design and the followed general methodology for each new algorithm. One of the most important challenges which are faced is to design these tools in a way that does not compromise the privacy of the clinical data involved. The speaker will show how to address the main questions when designing such algorithms: how to decompose and distribute the computations and what kind of information to exchange between nodes, in order to comply with the privacy constraint mentioned above. Finally, also the subject of validating these federated algorithms will be briefly touched.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 20:26
Speaker: : Jason Skellariou
The Medical Informatics Platform (MIP) Dementia had been installed in several memory clinics across Europe allowing them to federate their real-world databases. Research open access databases had also been integrated such as ADNI (Alzheimer’s Dementia Neuroimaging Initiative), reaching a cumulative case load of more than 5,000 patients (major cognitive disorder due to Alzheimer’s disease, other major cognitive disorder, minor cognitive disorder, controls). The statistic and machine learning tools implemented in the MIP allowed researchers to conduct easily federated analyses among Italian memory clinics (Redolfi et al. 2020) and also across borders between the French (Lille), the Swiss (Lausanne) and the Italian (Brescia) datasets.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 16:44
Speaker: : Mélanie Leroy
This talks presents ethics requirements of the Medical Informatics Platform, a data sharing platform for medical data using data federation mechanisms. The talk presents how the Medical Informatics Platform (MIP) works and which ethical requirements need to be considered when working with federated data.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 16:25
Speaker: : Erika Borcel
This lecture talks about the usage of knowledge graphs in hospitals and related challenges of semantic interoperability.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 24:32
Speaker: : Cristophe Gaudet-Blavignac
Topics
- Artificial Intelligence (7)
- Philosophy of Science (5)
- Provenance (3)
- protein-protein interactions (1)
- Extracellular signaling (1)
- Animal models (8)
- Assembly 2021 (29)
- Brain-hardware interfaces (14)
- Clinical neuroscience (40)
- International Brain Initiative (2)
- Repositories and science gateways (11)
- Resources (6)
- General neuroscience
(62)
- Neuroscience (11)
- Cognitive Science (7)
- Cell signaling (6)
- Brain networks (11)
- Glia (1)
- (-) Electrophysiology (41)
- Learning and memory (5)
- Neuroanatomy (24)
- Neurobiology (16)
- Neurodegeneration (1)
- Neuroimmunology (1)
- Neural networks (15)
- Neurophysiology (27)
- Neuropharmacology (2)
- Neuronal plasticity (16)
- Synaptic plasticity (4)
- Visual system (12)
- Phenome (1)
- General neuroinformatics
(27)
- Computational neuroscience (279)
- Statistics (7)
- Computer Science (21)
- Genomics (34)
- Data science
(34)
- Open science (61)
- Project management (8)
- Education (4)
- Publishing (4)
- Neuroethics (42)