Difficulty level
This lightning talk describes an automated pipline for positron emission tomography (PET) data.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 7:27
Speaker: : Soodeh Moallemian
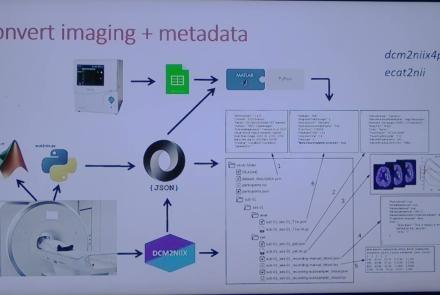
This session introduces the PET-to-BIDS (PET2BIDS) library, a toolkit designed to simplify the conversion and preparation of PET imaging datasets into BIDS-compliant formats. It supports multiple data types and formats (e.g., DICOM, ECAT7+, nifti, JSON), integrates seamlessly with Excel-based metadata, and provides automated routines for metadata updates, blood data conversion, and JSON synchronization. PET2BIDS improves human readability by mapping complex reconstruction names into standardized, descriptive labels and offers extensive documentation, examples, and video tutorials to make adoption easier for researchers.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 9:23
Speaker: : Cyril Pernet
This session introduces the PET-to-BIDS (PET2BIDS) library, a toolkit designed to simplify the conversion and preparation of PET imaging datasets into BIDS-compliant formats. It supports multiple data types and formats (e.g., DICOM, ECAT7+, nifti, JSON), integrates seamlessly with Excel-based metadata, and provides automated routines for metadata updates, blood data conversion, and JSON synchronization. PET2BIDS improves human readability by mapping complex reconstruction names into standardized, descriptive labels and offers extensive documentation, examples, and video tutorials to make adoption easier for researchers.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 41:04
Speaker: : Martin Nørgaard
This session dives into practical PET tooling on BIDS data—showing how to run motion correction, register PET↔MRI, extract time–activity curves, and generate standardized PET-BIDS derivatives with clear QC reports. It introduces modular BIDS Apps (head-motion correction, TAC extraction), a full pipeline (PETPrep), and a PET/MRI defacer, with guidance on parameters, outputs, provenance, and why Dockerized containers are the reliable way to run them at scale.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:05:38
Speaker: : Martin Nørgaard
This session introduces two PET quantification tools—bloodstream for processing arterial blood data and kinfitr for kinetic modeling and quantification—built to work with BIDS/BIDS-derivatives and containers. Bloodstream fuses autosampler and manual measurements (whole blood, plasma, parent fraction) using interpolation or fitted models (incl. hierarchical GAMs) to produce a clean arterial input function (AIF) and whole-blood curves with rich QC reports ready. TAC data (e.g., from PETPrep) and blood (e.g., from bloodstream) can be ingested using kinfitr to run reproducible, GUI-driven analyses: define combined ROIs, calculate weighting factors, estimate blood–tissue delay, choose and chain models (e.g., 2TCM → 1TCM with parameter inheritance), and export parameters/diagnostics. Both are available as Docker apps; workflows emphasize configuration files, reports, and standard outputs to support transparency and reuse.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:20:56
Speaker: : Granville Matheson
This lecture covers positron emission tomography (PET) imaging and the Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS), and how they work together within the PET-BIDS standard to make neuroscience more open and FAIR.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 12:06
Speaker: : Melanie Ganz
Course:
This module covers many of the types of non-invasive neurotech and neuroimaging devices including electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG), electroneurography (ENG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), and more.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 13:36
Speaker: : Harrison Canning
This brief talk goes into work being done at The Alan Turing Institute to solve real-world challenges and democratize computer vision methods to support interdisciplinary and international researchers.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 7:10
Speaker: : Alden Connor & Beatriz Costa Gomes
Course:
This book was written with the goal of introducing researchers and students in a variety of research fields to the intersection of data science and neuroimaging. This book reflects our own experience of doing research at the intersection of data science and neuroimaging and it is based on our experience working with students and collaborators who come from a variety of backgrounds and have a variety of reasons for wanting to use data science approaches in their work. The tools and ideas that we chose to write about are all tools and ideas that we have used in some way in our own research. Many of them are tools that we use on a daily basis in our work. This was important to us for a few reasons: the first is that we want to teach people things that we ourselves find useful. Second, it allowed us to write the book with a focus on solving specific analysis tasks. For example, in many of the chapters you will see that we walk you through ideas while implementing them in code, and with data. We believe that this is a good way to learn about data analysis, because it provides a connecting thread from scientific questions through the data and its representation to implementing specific answers to these questions. Finally, we find these ideas compelling and fruitful. That’s why we were drawn to them in the first place. We hope that our enthusiasm about the ideas and tools described in this book will be infectious enough to convince the readers of their value.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration:
Speaker: :
This lecture presents the Medical Informatic Platform's data federation for Traumatic Brain Injury.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 25:55
Speaker: : Stefano Finazzi
This lecture gives insights into the Medical Informatics Platform's current and future data privacy model.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 17:29
Speaker: : Yannis Ioannidis
This lecture explains the concept of federated analysis in the context of medical data, associated challenges. The lecture also presents an example of hospital federations via the Medical Informatics Platform.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 19:15
Speaker: : Yannis Ioannidis
This talk discusses what are usually considered successful outcomes of scientific research consortia, and how those outcomes can be translated into lasting impacts.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 18:24
Speaker: : Anita Bandrowski
In this lesson, you will learn about the BRAIN Initiative Cell Atlas Network (BICAN) and how this project adopts a federated approach to data sharing.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 11:23
Speaker: : Owen White
This talks presents an overview of the potential for data federation in stroke research.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 21:37
Speaker: : Maurizio A. Leone
This lecture explains the need for data federation in medicine and how it can be achieved.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 27:09
Speaker: : Philippe Ryvlin
Topics
- Artificial Intelligence (7)
- Philosophy of Science (5)
- Provenance (3)
- protein-protein interactions (1)
- Extracellular signaling (1)
- Animal models (8)
- Assembly 2021 (29)
- Brain-hardware interfaces (14)
- Clinical neuroscience (40)
- International Brain Initiative (2)
- Repositories and science gateways (11)
- Resources (6)
- General neuroscience
(62)
- Neuroscience (11)
- Cognitive Science (7)
- Cell signaling (6)
- Brain networks (11)
- Glia (1)
- Electrophysiology (41)
- Learning and memory (5)
- Neuroanatomy (24)
- Neurobiology (16)
- Neurodegeneration (1)
- Neuroimmunology (1)
- Neural networks (15)
- Neurophysiology (27)
- Neuropharmacology (2)
- Neuronal plasticity (16)
- Synaptic plasticity (4)
- Visual system (12)
- Phenome (1)
- General neuroinformatics
(27)
- Computational neuroscience (279)
- Statistics (7)
- Computer Science (21)
- Genomics (34)
- Data science
(34)
- Open science (61)
- Project management (8)
- Education (4)
- Publishing (4)
- Neuroethics (42)