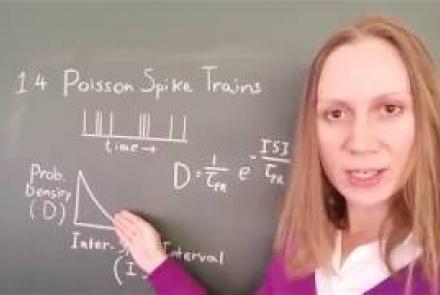Lesson type
Difficulty level
This lecture focuses on higher-level simulation scenarios using stimulation protocols. We demonstrate how to build stimulation patterns in TVB, and use them in a simulation to induced activity dissipating into experimentally known resting-state networks in human and mouse brain, a well as to obtain EEG recordings reproducing empirical findings of other researchers.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 47:14
Speaker: : Andreas Spiegler
This lecture presents the Graphical (GUI) and Command Line (CLI) User Interface of TVB. Alongside with the speakers, explore and interact with all means necessary to generate, manipulate and visualize connectivity and network dynamics.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:02:16
Speaker: : Paula Popa & Mihai Andrei
This lecture briefly introduces The Virtual Brain (TVB), a multi-scale, multi-modal neuroinformatics platform for full brain network simulations using biologically realistic connectivity, as well as its potential neuroscience applications (e.g., epilepsy cases).
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 8:53
Speaker: : Petra Ritter
This lecture introduces the theoretical background and foundations that led to the development of TVB, its architecture, and features of its major software components.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 46:50
Speaker: : Randy McIntosh
In this lesson, you will hear about the current challenges regarding data management, as well as policies and resources aimed to address them.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 18:13
Speaker: : Mojib Javadi
This lecture provides an overview of successful open-access projects aimed at describing complex neuroscientific models, and makes a case for expanded use of resources in support of reproducibility and validation of models against experimental data.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:00:39
Speaker: : Sharon Crook
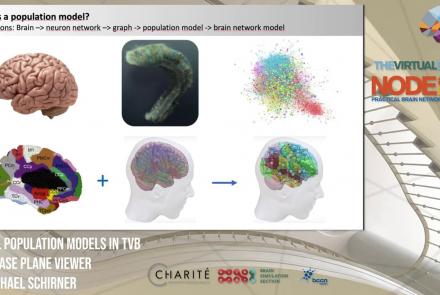
This lesson introduces population models and the phase plane, and is part of the The Virtual Brain (TVB) Node 10 Series, a 4-day workshop dedicated to learning about the full brain simulation platform TVB, as well as brain imaging, brain simulation, personalised brain models, and TVB use cases.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:10:41
Speaker: : Michael Schirner
This lesson introduces TVB-multi-scale extensions and other TVB tools which facilitate modeling and analyses of multi-scale data.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 36:10
Speaker: : Dionysios Perdikis
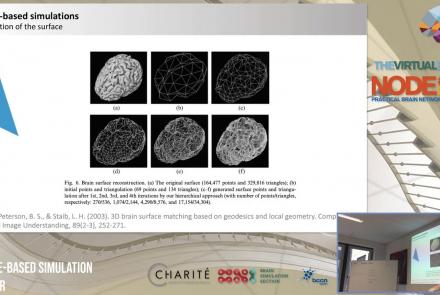
This lecture delves into cortical (i.e., surface-based) brain simulations, as well as subcortical (i.e., deep brain) stimulations, covering the definitions, motivations, and implementations of both.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 39:05
Speaker: : Jil Meier
This lecture provides an introduction to entropy in general, and multi-scale entropy (MSE) in particular, highlighting the potential clinical applications of the latter.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 39:05
Speaker: : Jil Meier
This lecture gives an overview of how to prepare and preprocess neuroimaging (EEG/MEG) data for use in TVB.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:40:52
Speaker: : Paul Triebkorn
In this lecture, you will learn about various neuroinformatic resources which allow for 3D reconstruction of brain models.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:36:57
Speaker: : Michael Schirner
This lecture provides an general introduction to epilepsy, as well as why and how TVB can prove useful in building and testing epileptic models.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 37:12
Speaker: : Julie Courtiol
This lecture on model types introduces the advantages of modeling, provide examples of different model types, and explain what modeling is all about.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 27:48
Speaker: : Gunnar Blohm
This lesson provides a brief introduction to the Computational Modeling of Neuronal Plasticity.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 0:40
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
In this lesson, you will be introducted to a type of neuronal model known as the leaky integrate-and-fire (LIF) model.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:23
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson goes over various potential inputs to neuronal synapses, loci of neural communication.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:20
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson describes the how and why behind implementing integration time steps as part of a neuronal model.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:08
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
In this lesson, you will learn about neural spike trains which can be characterized as having a Poisson distribution.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:18
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
This lesson covers spike-rate adaptation, the process by which a neuron's firing pattern decays to a low, steady-state frequency during the sustained encoding of a stimulus.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:26
Speaker: : Florence I. Kleberg
Topics
- Artificial Intelligence (6)
- Philosophy of Science (5)
- Notebooks (1)
- (-) Provenance (1)
- protein-protein interactions (1)
- Extracellular signaling (1)
- Animal models (2)
- Assembly 2021 (27)
- Brain-hardware interfaces (13)
- Clinical neuroscience (23)
- International Brain Initiative (2)
- Repositories and science gateways (5)
- Resources (5)
- General neuroscience
(17)
- General neuroinformatics
(5)
- (-) Computational neuroscience (101)
- Statistics (2)
- Computer Science (7)
- Genomics (3)
- Data science
(14)
- Open science (12)
- Project management (7)
- Education (1)
- Neuroethics (28)