Lesson type
Difficulty level
This lightning talk describes an automated pipline for positron emission tomography (PET) data.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 7:27
Speaker: : Soodeh Moallemian
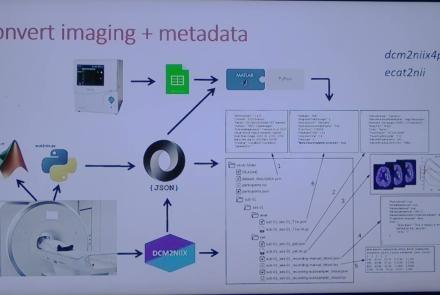
This session introduces the PET-to-BIDS (PET2BIDS) library, a toolkit designed to simplify the conversion and preparation of PET imaging datasets into BIDS-compliant formats. It supports multiple data types and formats (e.g., DICOM, ECAT7+, nifti, JSON), integrates seamlessly with Excel-based metadata, and provides automated routines for metadata updates, blood data conversion, and JSON synchronization. PET2BIDS improves human readability by mapping complex reconstruction names into standardized, descriptive labels and offers extensive documentation, examples, and video tutorials to make adoption easier for researchers.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 9:23
Speaker: : Cyril Pernet
This session introduces the PET-to-BIDS (PET2BIDS) library, a toolkit designed to simplify the conversion and preparation of PET imaging datasets into BIDS-compliant formats. It supports multiple data types and formats (e.g., DICOM, ECAT7+, nifti, JSON), integrates seamlessly with Excel-based metadata, and provides automated routines for metadata updates, blood data conversion, and JSON synchronization. PET2BIDS improves human readability by mapping complex reconstruction names into standardized, descriptive labels and offers extensive documentation, examples, and video tutorials to make adoption easier for researchers.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 41:04
Speaker: : Martin Nørgaard
This session dives into practical PET tooling on BIDS data—showing how to run motion correction, register PET↔MRI, extract time–activity curves, and generate standardized PET-BIDS derivatives with clear QC reports. It introduces modular BIDS Apps (head-motion correction, TAC extraction), a full pipeline (PETPrep), and a PET/MRI defacer, with guidance on parameters, outputs, provenance, and why Dockerized containers are the reliable way to run them at scale.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:05:38
Speaker: : Martin Nørgaard
This session introduces two PET quantification tools—bloodstream for processing arterial blood data and kinfitr for kinetic modeling and quantification—built to work with BIDS/BIDS-derivatives and containers. Bloodstream fuses autosampler and manual measurements (whole blood, plasma, parent fraction) using interpolation or fitted models (incl. hierarchical GAMs) to produce a clean arterial input function (AIF) and whole-blood curves with rich QC reports ready. TAC data (e.g., from PETPrep) and blood (e.g., from bloodstream) can be ingested using kinfitr to run reproducible, GUI-driven analyses: define combined ROIs, calculate weighting factors, estimate blood–tissue delay, choose and chain models (e.g., 2TCM → 1TCM with parameter inheritance), and export parameters/diagnostics. Both are available as Docker apps; workflows emphasize configuration files, reports, and standard outputs to support transparency and reuse.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 1:20:56
Speaker: : Granville Matheson
This lecture covers positron emission tomography (PET) imaging and the Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS), and how they work together within the PET-BIDS standard to make neuroscience more open and FAIR.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 12:06
Speaker: : Melanie Ganz
Course:
This module covers many of the types of non-invasive neurotech and neuroimaging devices including electroencephalography (EEG), electromyography (EMG), electroneurography (ENG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), and more.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 13:36
Speaker: : Harrison Canning
This lecture covers the three big questions: What is the universe?, what is life?, and what is consciousness?
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:07:52
Speaker: : Paul F.M.J. Verschure
This lecture outlines various approaches to studying Mind, Brain, and Behavior.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:02:34
Speaker: : Paul F.M.J. Verschure
This lecture covers the history of behaviorism and the ultimate challenge to behaviorism.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:19:08
Speaker: : Paul F.M.J. Verschure
This lecture covers various learning theories.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:00:42
Speaker: : Paul F.M.J. Verschure
Course:
An introduction to data management, manipulation, visualization, and analysis for neuroscience. Students will learn scientific programming in Python, and use this to work with example data from areas such as cognitive-behavioral research, single-cell recording, EEG, and structural and functional MRI. Basic signal processing techniques including filtering are covered. The course includes a Jupyter Notebook and video tutorials.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:09:16
Speaker: : Aaron J. Newman
Course:
The goal of computational modeling in behavioral and psychological science is using mathematical models to characterize behavioral (or neural) data. Over the past decade, this practice has revolutionized social psychological science (and neuroscience) by allowing researchers to formalize theories as constrained mathematical models and test specific hypotheses to explain unobservable aspects of complex social cognitive processes and behaviors. This course is composed of 4 modules in the format of Jupyter Notebooks. This course comprises lecture-based, discussion-based, and lab-based instruction. At least one-third of class sessions will be hands-on. We will discuss relevant book chapters and journal articles, and work with simulated and real data using the Python programming language (no prior programming experience necessary) as we survey some selected areas of research at the intersection of computational modeling and social behavior. These selected topics will span a broad set of social psychological abilities including (1) learning from and for others, (2) learning about others, and (3) social influence on decision-making and mental states. Rhoads, S. A. & Gan, L. (2022). Computational models of human social behavior and neuroscience - An open educational course and Jupyter Book to advance computational training. Journal of Open Source Education, 5(47), 146. https://doi.org/10.21105/jose.00146
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration:
Speaker: :
This brief video provides a welcome and short introduction to the outline of the INCF Short Course in Neuroinformatics, held Seattle, Washington in October 2023, in coordination with the West Big Data Hub and the University of Washington.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 4:58
Speaker: : Ariel Rokem
Course:
This lecture will provide an overview of the INCF Training Suite, a collection of tools that embraces the FAIR principles developed by members of the INCF Community. This will include an overview of TrainingSpace, Neurostars, and KnowledgeSpace.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 09:50
Speaker: : Mathew Abrams
Course:
The International Brain Initiative (IBI) is a consortium of the world’s major large-scale brain initiatives and other organizations with a vested interest in catalyzing and advancing neuroscience research through international collaboration and knowledge sharing. This workshop introduces the IBI, the efforts of the Data Standards and Sharing Working Group, and keynote lectures on the impact of data standards and sharing on large-scale brain projects, as well as a discussion on prospects and needs for neural data sharing.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 2:06:58
Course:
KnowledgeSpace (KS) is a data discoverability portal and neuroscience encyclopedia that was developed to make it easier for the neuroscience community to find publicly available datasets that adhere to the FAIR Principles and to provide an integrated view of neuroscience concepts found in Wikipedia and NeuroLex linked with PubMed and 17 of the world's leading neuroscience repositories. In short, KS provides a single point of entry where reseaerchers can search for a neuroscience concept of interest and receive results that include: i. a description of the term found in Wikipedia/NeuroLex, ii. links to publicly available datasets related to the concept of interest, and iii. up-to-date references that support the concept of interests found in PubMed. APIs are available so that developers of other neuroscience research infrastructures can integrate KS components in their infrastructures. If your repository or your favorite repository is not indexed in KS, please contact us.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 6:14
Speaker: : Heather Topple
Topics
- Artificial Intelligence (7)
- Philosophy of Science (5)
- Provenance (3)
- protein-protein interactions (1)
- Extracellular signaling (1)
- Animal models (8)
- Assembly 2021 (29)
- Brain-hardware interfaces (14)
- Clinical neuroscience (40)
- International Brain Initiative (2)
- Repositories and science gateways (11)
- Resources (6)
- General neuroscience
(62)
- Neuroscience (11)
- Cognitive Science (7)
- Cell signaling (6)
- Brain networks (11)
- Glia (1)
- Electrophysiology (41)
- Learning and memory (5)
- Neuroanatomy (24)
- Neurobiology (16)
- Neurodegeneration (1)
- Neuroimmunology (1)
- Neural networks (15)
- Neurophysiology (27)
- Neuropharmacology (2)
- Neuronal plasticity (16)
- Synaptic plasticity (4)
- Visual system (12)
- Phenome (1)
- General neuroinformatics
(27)
- Computational neuroscience (279)
- Statistics (7)
- Computer Science (21)
- Genomics (34)
- Data science
(34)
- Open science (61)
- Project management (8)
- (-) Education (4)
- Publishing (4)
- Neuroethics (42)