Course:
This lesson introduces the EEGLAB toolbox, as well as motivations for its use.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 15:32
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
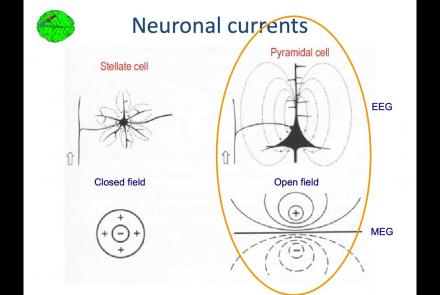
Course:
In this lesson, you will learn about the biological activity which generates and is measured by the EEG signal.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 6:53
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
This lesson goes over the characteristics of EEG signals when analyzed in source space (as opposed to sensor space).
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 10:56
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
This lesson describes the development of EEGLAB as well as to what extent it is used by the research community.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 6:06
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
This lesson provides instruction as to how to build a processing pipeline in EEGLAB for a single participant.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 9:20
Speaker: :
Course:
Whereas the previous lesson of this course outlined how to build a processing pipeline for a single participant, this lesson discusses analysis pipelines for multiple participants simultaneously.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 10:55
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
In addition to outlining the motivations behind preprocessing EEG data in general, this lesson covers the first step in preprocessing data with EEGLAB, importing raw data.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 8:30
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
Continuing along the EEGLAB preprocessing pipeline, this tutorial walks users through how to import data events as well as EEG channel locations.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 11:53
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
This tutorial demonstrates how to re-reference and resample raw data in EEGLAB, why such steps are important or useful in the preprocessing pipeline, and how choices made at this step may affect subsequent analyses.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 11:48
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
This tutorial instructs users how to visually inspect partially pre-processed neuroimaging data in EEGLAB, specifically how to use the data browser to investigate specific channels, epochs, or events for removable artifacts, biological (e.g., eye blinks, muscle movements, heartbeat) or otherwise (e.g., corrupt channel, line noise).
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 5:08
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
This tutorial provides instruction on how to use EEGLAB to further preprocess EEG datasets by identifying and discarding bad channels which, if left unaddressed, can corrupt and confound subsequent analysis steps.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 13:01
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
Users following this tutorial will learn how to identify and discard bad EEG data segments using the MATLAB toolbox EEGLAB.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 11:25
Speaker: : Arnaud Delorme
Course:
An introduction to data management, manipulation, visualization, and analysis for neuroscience. Students will learn scientific programming in Python, and use this to work with example data from areas such as cognitive-behavioral research, single-cell recording, EEG, and structural and functional MRI. Basic signal processing techniques including filtering are covered. The course includes a Jupyter Notebook and video tutorials.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 1:09:16
Speaker: : Aaron J. Newman
The Allen Mouse Brain Atlas is a genome-wide, high-resolution atlas of gene expression throughout the adult mouse brain. This tutorial describes the basic search and navigation features of the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 6:40
Speaker: : Allen Institute for Brain Science
The Allen Developing Mouse Brain Atlas is a detailed atlas of gene expression across mouse brain development. This tutorial describes the basic search and navigation features of the Allen Developing Mouse Brain Atlas.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 6:35
Speaker: : Unknown
This tutorial demonstrates how to use the differential search feature of the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas to find gene markers for different regions of the brain, as well as to visualize this gene expression in three-dimensional space. Differential search is also available for the Allen Developing Mouse Brain Atlas and the Allen Human Brain Atlas.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 6:31
Speaker: : Unknown
This lecture provides an introduction to optogenetics, a biological technique to control the activity of neurons or other cell types with light.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 39:34
Speaker: : Adam Packer
Course:
Longitudinal Online Research and Imaging System (LORIS) is a web-based data and project management software for neuroimaging research studies. It is an open source framework for storing and processing behavioural, clinical, neuroimaging and genetic data. LORIS also makes it easy to manage large datasets acquired over time in a longitudinal study, or at different locations in a large multi-site study.
Difficulty level: Beginner
Duration: 0:35
Speaker: : Samir Das
Course:
This lecture covers the rationale for developing the DAQCORD, a framework for the design, documentation, and reporting of data curation methods in order to advance the scientific rigour, reproducibility, and analysis of data.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 17:08
Speaker: : Ari Ercole
The Medical Informatics Platform (MIP) is a platform providing federated analytics for diagnosis and research in clinical neuroscience research. The federated analytics is possible thanks to a distributed engine that executes computations and transfers information between the members of the federation (hospital nodes). In this talk the speaker will describe the process of designing and implementing new analytical tools, i.e. statistical and machine learning algorithms. Mr. Sakellariou will further describe the environment in which these federated algorithms run, the challenges and the available tools, the principles that guide its design and the followed general methodology for each new algorithm. One of the most important challenges which are faced is to design these tools in a way that does not compromise the privacy of the clinical data involved. The speaker will show how to address the main questions when designing such algorithms: how to decompose and distribute the computations and what kind of information to exchange between nodes, in order to comply with the privacy constraint mentioned above. Finally, also the subject of validating these federated algorithms will be briefly touched.
Difficulty level: Intermediate
Duration: 20:26
Speaker: : Jason Skellariou
Topics
- Standards and Best Practices (3)
- Provenance (2)
- Artificial Intelligence (1)
- protein-protein interactions (1)
- Extracellular signaling (1)
- Animal models (2)
- Assembly 2021 (6)
- Brain-hardware interfaces (12)
- (-) Clinical neuroscience (3)
- Repositories and science gateways (1)
- Resources (3)
- General neuroscience (16)
- Phenome (1)
- General neuroinformatics
(1)
- Computational neuroscience (95)
- Statistics (5)
- Computer Science (6)
- Genomics (31)
- (-) Data science (19)
- Open science (33)
- Project management (1)
- Education (2)
- Publishing (1)
- Neuroethics (1)